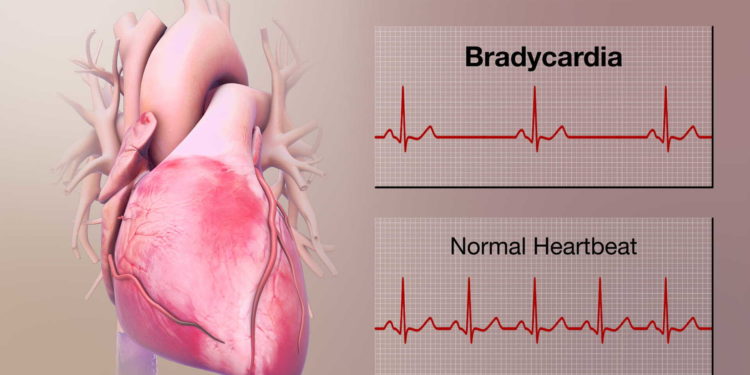
Bradycardia Definition is that it is an abnormally low heart rate, commonly described as a resting heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute in adults. It is a disturbance in the Normal Heart Rate of an Adult. Symptoms of this illness may include weakness, exhaustion, dizziness, fainting, and dyspnea. Many things, such as underlying cardiac disorders, drugs, electrolyte imbalances, or specific medical treatments, can result in bradycardia.
Moreover, the fundamental reason, the degree of symptoms, and the general health of the patient all play a role in determining whether bradycardia is serious or harmful. Bradycardia may not always result in symptoms or problems and may go untreated. However, bradycardia can be significant and need medical care if it causes symptoms like exhaustion, dizziness, fainting, or shortness of breath, or if it signals an underlying cardiac disease.
Bradycardia can also result in problems like reduced blood flow to essential organs, which, if not addressed, can cause fainting, low blood pressure, or even cardiac arrest. For this reason, anyone having Symptoms of Bradycardia must seek medical attention to identify the underlying cause and the best course of action.
Bradycardia Definition: Symptoms

Bradycardia, or an unusually low heart rate, can cause a variety of Symptoms of Bradycardia,
Fatigue: Excessively worn out or lethargic, even after getting enough sleep.
Feeling shaky or faint: This sensation is more common while getting up rapidly.
Syncope: A temporary loss of consciousness brought on by a reduction in blood supply to the brain.
Shortness of breath: Breathlessness or difficulty breathing, particularly during physical activity can also be one of the Symptoms of Bradycardia.
Chest pain: Tightness or discomfort in the chest region, although it’s not a constant symptom.
Weakness: Experiencing physical weakness or being unable to carry out daily tasks.
Confusion: Having trouble focusing or feeling disoriented mentally.
Palpitations: the sensation of rapid, irregular heartbeats.
Exercise intolerance: a reduced tolerance for physical activity or difficulty exercising.
Nausea: Experiencing gastrointestinal distress or feeling ill in the stomach.
Here an important thing to remember is that not everyone with bradycardia will have symptoms and that symptoms can differ in intensity based on some variables, including the underlying reason, the severity of the bradycardia, and the general health of the person. It is important to get medical attention if you meet any of these symptoms, especially if they are severe or chronic, to identify the underlying reason and the best course of action.
Causes of Bradycardia
Aging: A person’s heart may naturally slow down as they age due to a slowing electrical system in their heart.
Cardiac problems: Bradycardia can result from certain cardiac disorders that interfere with the heart’s electrical signals, such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction (heart attack), heart failure, or cardiomyopathy.
Medication: Slowing the heart rate is a side effect of several drugs, including beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics, and several antidepressants.
Electrolyte imbalances: The electrical activity of the heart can be impacted by abnormal blood levels of electrolytes, such as hypokalemia (low potassium) or hypomagnesemia (low magnesium), which can lead to bradycardia.
Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid gland: Thyroid hormones are essential for controlling heart rate and metabolism. Bradycardia and other symptoms might result from low thyroid hormone levels.
Diseases: Several infections can impact the heart’s electrical system and result in bradycardia. These include myocarditis, which is an inflammation of the heart muscle, and endocarditis, which is an infection of the heart valves.
Congenital heart defects: Bradycardia can result from an individual’s birth defects, which are structural irregularities of the heart that impact its electrical conduction system.
Hypothermia: Abnormally low body temperature can cause bradycardia and a slowing of the heart rhythm.
Certain medical treatments: The electrical system of the heart can occasionally be disrupted by medical procedures including heart surgery, catheter ablation, or the insertion of cardiac devices like pacemakers, which can result in either temporary or permanent bradycardia.
Individual differences can exist in the Bradycardia Signs; therefore, a comprehensive medical evaluation is required to identify the cause and the best course of treatment.