Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a disorder that causes the immune system to not make enough antibodies, which can result in regular infections and other health issues. It is the immunity that protects a lot of factors. So when it is not enough, the condition puts people at serious risk.
Visualize having a protection that lacks the necessary saving skills. Living with Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) is like that. This illness indicates that your immune system, which is meant to keep you safe from infections, isn’t functioning at its best. Individuals with immunodeficiency CVID have a higher risk of disease due to compromised immune systems.
If we simply put what is common variable immunodeficiency, these diseases affect the immune system’s capacity to battle illnesses and infections. Primary immunodeficiency CVID disorders, which result from genetic mutations, or secondary immunodeficiency diseases, which result from external factors such as infections or drugs, can cause this disability. These illnesses make people more vulnerable to illnesses, infections, and problems that a healthy immune system would normally be able to keep away.
The immune system has great significance in life. To protect the body from pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, the immune system is essential. It also helps to recognize abnormal cells, including cancer cells, and destroy them. Immune system dysfunction, such as immunodeficiency CVID illnesses, impairs the body’s capacity to identify and react to threats, making the body more vulnerable to disease.
Furthermore, the body’s initial line of defense against infections is innate immunity. It consists of immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages that recognize and consume infections, as well as physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes. Although innate immunity is not pathogen-specific, it reacts swiftly.
Adaptive Immunity offers a more targeted response as it matures. It involves lymphocytes, such as T cells, which assist in controlling the immune response and eradicate infected cells directly, and B cells, which generate antibodies that target particular antigens. Adaptive immunity produces memory cells that offer persistent defense against infections that have previously been encountered.
Immune cell receptors that identify particular molecular patterns linked to illnesses help the immune system identify invaders. The immune system launches a reaction when a pathogen is found, using a variety of cells and proteins to neutralize and eradicate the threat. Together, the innate and adaptive immune responses offer a complete defense.
Nonetheless, Common variable immunodeficiency is one of the key immunodeficiencies that are detected more commonly. Low amounts of antibodies, which are proteins produced by the immune system to fend off infections, are seen in people with immunodeficiency CVID. They are therefore more prone to infections, particularly those of the sinuses, lungs, and ears.
Signs and symptoms of Common variable immunodeficiency
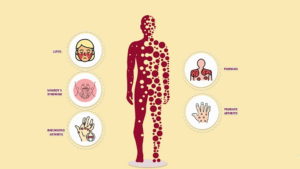
Although each person’s symptoms of CVID are unique, frequent indications include:
- Periodic infections, particularly in the ears, sinuses, and lungs
- Stubborn coughing and dyspnea
- Constant diarrhea and digestive problems
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion and an overall sensation of illness
- Autoimmune diseases, in which the body’s own tissues, are attacked by the immune system
Causes of common immunodeficiency disease
Although the precise origin of CVID is unknown, environmental and genetic factors are thought to play a role. Although it can run in families, indicating a hereditary component, the precise genes implicated are frequently unknown. There have been instances where immune system-related gene alterations have been found.
Although having an immunodeficiency such as CVID might be difficult, there are ways to manage the illness and keep a high standard of living:
- Frequent Medical Check-ups: Make sure you visit your healthcare provider regularly to stay on top of your health.
- Immunoglobulin Therapy: Regular immunoglobulin treatment helps strengthen your body’s defenses against illness.
- Healthy Lifestyle: To build your body, eat a balanced diet, exercise frequently, and get adequate sleep.
- Keep your immunizations up to date, limit contact with sick people, and practice proper hygiene to prevent infections.
- Keep an eye on your symptoms: Make a note of any new or worsening symptoms, and notify your physician right once.
- Stress management: Find ways to decompress by practicing yoga, meditation, or engaging in enjoyable hobbies.
- Support System: Make connections with people who are experiencing comparable circumstances or join support groups.
- Education: To effectively manage your condition, learn everything you can about it.
- Medication Adherence: Follow your doctor’s instructions and take all recommended drugs.
- Prepare an emergency plan to handle serious infections or medical emergencies.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests

Blood testing: A vital diagnostic tool for immunodeficiencies. These tests can evaluate the general health of the immune system and measure the quantities of different immune cells and antibodies.
Genetic testing: Provides an accurate diagnosis and facilitates family planning by identifying particular genetic variants linked to primary immunodeficiencies.
Immunological tests: Assess the immune system’s performance, encompassing assays for particular antibody reactions and complement system activity.
Nevertheless, there can be Coping strategies including methods like cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychotherapy, and stress management that help people deal with the emotional effects of having a chronic illness.
Understanding Common variable immunodeficiency is important. Put your health first and do everything possible to have things easy and sorted for you.












