Neurofeedback therapy is a different and non-invasive approach to treating mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, ADHD, and more. Real-time feedback on brain activity is used in this innovative treatment to assist patients in controlling their brain activity and enhancing their mental health. ADHD, as well as other disorders like epilepsy, anxiety, depression, and insomnia, are frequently treated using neurofeedback.
Additionally, it is being investigated for learning impairments, drug addiction, schizophrenia, and autistic spectrum disorder.
Although this therapy has been used for a long time, there is still ongoing and differing research regarding its effectiveness. It isn’t a cure-all, but it might benefit certain patients.
Instead of being a stand-alone treatment, the Neurofeedback therapy is frequently most effective when used in combination with other recognized therapies.
Nonetheless, EEG biofeedback, another name for Neurofeedback therapy, is a type of brain training. It involves tracking the electrical activity (brainwaves) in your brain and giving you immediate feedback so you can learn to control how your brain works on its own. Better focus, mood stability, and a decrease in the symptoms of mental health illnesses can result from this therapy’s support in reskilling the brain to operate more effectively.
Furthermore, Depending on the condition and individual response, it may take longer, but many patients see improvement in 10–20 sessions.
Indeed, this process is thought to be safe and has few negative consequences. There is no medicine involved, and it is non-invasive.
Indeed, for a more thorough approach to mental health care, neurofeedback is frequently used in conjunction with other therapies like counseling or medication.
The Science of Neurofeedback Therapy
Brainwaves are the electrical impulses that your brain continuously produces. Various mental states are linked to distinct brainwaves:
- Focus and active thought are associated with beta waves.
- Calm and relaxation are associated with alpha waves.
- Theta waves are frequently seen during light sleep and daydreaming.
- Deep sleep is when delta waves happen.
These brainwaves are measured by sensors applied to your scalp during neurofeedback therapy. After that, the data is shown on a screen, giving you a real-time view of how your brain is working.
You can train your brain to work better by engaging in different games or activities that provide you with feedback when your brain generates the proper brainwaves, typically in the form of sounds or visual signals.
What Is the Process of Neurofeedback Therapy?
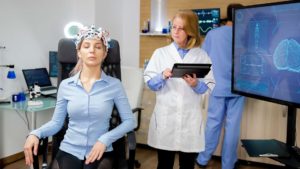
First Evaluation: First, an EEG (electroencephalogram) equipment maps your brainwaves as part of an initial brain assessment. Neurofeedback therapy helps the therapist determine which patterns of brainwaves require modification.
Feedback & Training: Sensors are applied to your scalp as you sit in a comfortable chair for each Neurofeedback therapy session. A screen that shows your brain activity in real-time will be displayed to you. Usually, the feedback takes the shape of a video game, noises, or visuals that respond to your brain activity. For instance, you may notice a character in a game advance or a film become clearer if your brainwaves shift into a more relaxed or concentrated condition.
Learning and Repetition: Your brain can learn to generate better brainwave patterns on its own with consistent practice. Repetition strengthens these neural networks, resulting in long-lasting changes in brain function, much like when learning a new skill.
Improvement over Time: Depending on the disease being treated, long-term benefits may necessitate several sessions of Neurofeedback therapy spread out over a few weeks or months, although most people experience gradual improvements after a few sessions.
Disorders Neurofeedback Therapy Treats
Numerous mental health conditions are treated using this therapy. Among the most prevalent disorders are:
Anxiety: Neurofeedback soothes the hyperactive parts of the brain that cause excessive stress and concern.
Depression: This therapy can help control mood and enhance emotional stability by encouraging healthier brainwave patterns.
Neurofeedback for ADHD: Because it helps increase focus, decrease impulsivity, and improve concentration without the need for medication, this therapy is particularly well-liked for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Sleep Disorders: By teaching the brain to enter the proper resting states, this method can assist control sleep patterns.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): This therapy may lessen the severity of PTSD symptoms, such as hypervigilance and emotional dysregulation, by assisting in the retraining of brainwave activity.
Addictions: Fundamental brain dysfunction that fuels addictive behaviors can also be addressed with neurofeedback.
Advantages of Neurofeedback training

Drug-free and non-intrusive: The fact that this therapy doesn’t require drugs or invasive procedures is one of its biggest benefits. It only makes use of your brain’s inborn ability to adapt and learn.
Personalized Care: Because every person’s brain is different, these sessions are customized to fit your needs depending on the results of your initial brainwave analysis.
Few Side Effects: When compared to pharmaceuticals, this therapy has very few side effects. After sessions, the majority of people just have slight headaches or temporary tiredness.
Long-Term Benefits: The brain eventually learns to sustain better habits on its own, which may improve symptoms over time.
Helps with several mental health Conditions: Neurofeedback is adaptable and may be used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, ADHD, and more.
What can you expect during a neurofeedback therapy session?
Sessions of this therapy are usually calm and comfortable. Here’s a broad overview of what happens:
Each session lasts between thirty and sixty minutes.
Relaxation: The therapist applies sensors to your scalp while you sit in a comfortable chair. Only your brain activity is measured by these painless sensors.
Training: A screen that responds to your brainwaves will be displayed to you. For instance, as your brainwaves shift into the appropriate state, you might play a simple video game or watch a movie that becomes brighter or faster.
Repetition: Depending on the condition being treated, most people require 20–40 neurofeedback training sessions to achieve the best results.
Furthermore, Neurofeedback is particularly beneficial for people looking for a non-invasive, non-medical method of treating mental health issues. To find out if this therapy is right for you, it’s fundamental to speak with a medical professional or neurofeedback expert. Although it can be a successful stand-alone treatment, it is frequently used with more conventional therapies like counseling and medicine.
Neurofeedback may not be effective for everyone, which could result in time and financial waste.
Although the therapy is generally risk-free, drowsiness, agitation, anxiety, cognitive interference, or irritation are possible opposing effects.
While drowsiness may be a benefit, especially for those who have trouble sleeping, headset discomfort is also a regular minor problem.
Monitoring symptoms and brain activity at the start and finish of each session, as well as keeping an eye on the patient’s condition in between sessions to make sure improvement is occurring, are common ways to assess progress.
Neurofeedback therapy is expected to play a significant role in the future of mental health care. To guarantee appropriate training and minimize hazards, it’s important to collaborate with a certified practitioner.












