A Brain aneurysm is an expansion or bulge in a brain blood artery. Just as water flows through a weak area in a garden tube to make a bubble, the weakening of a blood vessel in the brain can cause it to bulge and form an aneurysm. The majority of Brain aneurysms are gentle and rarely cause symptoms, but rarely do they burst, causing a serious risk to life and health. Early detection of this condition and its symptoms is crucial since it can help prevent serious consequences.
Simply put, when a weak or thin patch develops on a blood vessel in the brain, it can cause the vessel to bulge or balloon out, which is known as a cerebral aneurysm or Brain aneurysm. Problems may arise if this bulge presses on brain tissue or nerves. The surrounding area of the brain is exposed to blood if the aneurysm bursts or ruptures. This is known as a hemorrhage, and it may result in fatalities or other severe conditions including a stroke, brain injury, a coma, or even death.
Certain aneurysms, particularly those that are little, don’t create any problems. When doing testing for other medical purposes, Brain aneurysms are often accidentally discovered. Although they can form anywhere in the brain, aneurysms most commonly occur in the arteries close to the base of the skull. Although not all aneurysms burst, they all have the risk of doing so, which can result in potentially fatal hemorrhage, horribly threatening to health of a person.
A Brain aneurysm can be tiny or enormous in size, and because of the high blood pressure in these locations, they usually form at the places where arteries branch.
It is estimated that between 3 and 5% of people have Brain aneurysms, but very few of these will burst.
Brain aneurysm symptoms
Brain aneurysms that have not ruptured may show no symptoms at all. Nonetheless, the aneurysm may have visible symptoms as it enlarges or exerts pressure on surrounding tissues and nerves.
Aneurysm without rupture
An unruptured Brain aneurysm may cause the following symptoms:
- Small aneurysms may remain silent.
- Bigger ones could put pressure on the nerves and brain, leading to:
- Discomfort behind or above the eyes
- Numbness
- Paralysis or weakness on one cheek side
- A dilated pupil (the area of the eye that is black)
- Issues with eyesight or double vision
Aneurysm rupture
A sudden, intense headache that is frequently referred to as “the worst headache of your life”
- Dual vision
- Vomiting and nausea
- Rigid neck
- Light Sensitivity
- Seizures (trembling without control)
- Unconsciousness (passing out)
- Arrest of the heart (heart stops beating)
Brain aneurysm that is seeping
An aneurysm may occasionally leak a small amount of blood before completely rupturing. Days or weeks before a significant rupture, this may result in a warning headache. This, however, is a rare occurrence.
Seek immediate medical attention if you have any of these symptoms along with an abrupt, intense headache.
The symptoms of a ruptured Brain aneurysm are often abrupt and severe, and it’s a medical emergency.
If you or anybody else encounters these symptoms, get emergency medical attention right once.
Types of Brain aneurysm
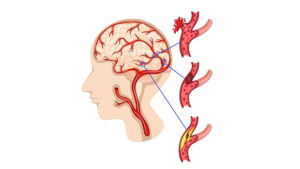
There are three categories of cerebral aneurysms:
Saccular aneurysm: The most prevalent form is a saccular aneurysm, also known as a Berry aneurysm. It resembles a tiny, spherical sac that is secure to a blood vessel, like a berry on a vine.
Fusiform aneurysm: A blood vessel that has a fusiform aneurysm will bulge on both sides.
Mycotic Aneurysm: An infection that weakens the blood artery wall causes this type to occur.
Brain aneurysm Size
- Tiny: Measuring less than 11 millimeters, or around the size of a large pencil eraser
- Big: 11–25 millimeters (about the same width as a dime)
- Greater than 25 millimeters (wider than a quarter) is considered giant.
Brain aneurysm causes
A Brain aneurysm may occur as a result of various circumstances, such as:
Hypertension: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, increases the risk of aneurysms by applying additional pressure to the artery walls.
Atherosclerosis: The artery walls may become weaker due to plaque accumulation.
Genetic factors: Due to family history, certain persons are born with an increased risk of aneurysms.
Trauma or injury: Head trauma can result in the formation of an aneurysm.
Infections: Several blood vessel-related infections have been linked to aneurysms.
Lifestyle factors: There is a correlation between an increased risk of aneurysm formation and smoking, heavy alcohol use, and drug usage.
Gender and age: Women are somewhat more likely than men to experience Brain aneurysms, with persons over 40 having a higher incidence rate.
Can you survive a Brain Aneurysm?
Whether or not an aneurysm in the Brain has ruptured is a major factor in determining its survival rate. The prediction for unruptured aneurysms is usually favorable if they are discovered early. Many can be managed with surgery or monitoring before they cause significant harm.
A ruptured aneurysm, on the other hand, presents a far more dangerous scenario. About two-thirds of survivors suffer chronic neurological impairment, and about 40% of burst Brain aneurysms are fatal. The likelihood of survival is significantly increased by early discovery and quick medical intervention, such as surgery or endovascular treatment.
Brain aneurysm how does it happen?
When the blood artery walls in the brain weaken and thin, aneurysms can develop. They generally occur at branch sites where blood arteries divide, which are naturally weaker locations.
Although aneurysms can occur in any age group, Brain aneurysms are more common in women and adults between the ages of 30 and 60. Certain individuals have inherited disorders that increase their risk of developing aneurysms.
Brain aneurysm Development Risk Factors are inherited (transmitted within families), genetic conditions that cause arterial walls to deteriorate, kidney illness known as polycystic kidney disease, in which the kidneys develop many cysts, Blood flow is disrupted by twisted blood arteries in the brain, known as arteriovenous malformations.
Furthermore, Brain tumors, blood vessel infections, and head injuries are some other, less frequent reasons.
How Can a Brain aneurysm be diagnosed?
The majority of Brain aneurysms are not detected until they burst or become apparent during examinations for other illnesses. Your doctor will prescribe tests to check for brain bleeding if you have symptoms like a severe headache. Typical testing consists of the following:
- CT scan: A type of X-ray in which the brain is finely mapped out.
- MRI: A scan that creates finely detailed images of the brain using radio waves and magnets.
- A technique called cerebral angiography allows a physician to visualize the blood arteries in the brain by injecting dye into the patient’s circulation.
- Spinal tap: To check for bleeding, a physician takes a little sample of fluid from the spine.
An important thing to note is the consequences of a Ruptured Brain aneurysm. When an aneurysm ruptures, it can cause potentially fatal consequences like:
- Rebleeding: If the Brain aneurysm bursts again before receiving treatment, further harm may result.
- Changes in sodium levels: Bleeding can have an impact on the sodium balance in the brain, which can cause swelling and damage to the brain.
- A buildup of fluid in the brain that increases pressure and can result in brain damage or even death is called hydrocephalus.
- Vasospasm: A narrowing of the blood arteries in the brain can lower blood flow and result in a stroke.
- Seizures: Medication may be required to manage seizures resulting from aneurysm bleeding.
Nonetheless, a Brain aneurysm may not cause any symptoms at first, but it might potentially turn fatal. It’s important to be aware and get regular checks if you have risk factors like high blood pressure, smoking, or a family history of aneurysms. This will help to identify any possible problems early.
To determine why certain individuals are subject to Brain aneurysms, scientists are investigating the genetics of the condition. Additionally, new techniques are being developed to identify aneurysms early, before they burst.